Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)
CLL
Know where you stand
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a type of leukemia that affects B cells that are fully developed. This type of leukemia tends to grow more slowly than most other types of the disease. CLL is often diagnosed in patients through routine blood work, and treatment is often delayed until the patient shows symptoms of the disease. These symptoms may include enlarged lymph nodes in the neck or underarms, fevers, night sweats, frequent infections, and enlarged spleen and/or liver.1
Any amount of residual disease may mean an increased risk that your cancer will get worse.2 Even though CLL is a relatively slow-moving disease, it may be important to be sure of your exact MRD status at key points in your care. This information may help you and your doctor to make informed decisions about your care plan.

clonoSEQ patient brochure
When should you monitor with clonoSEQ®?
Monitoring MRD throughout your cancer journey can help detect changes in your disease. For example, if your treatment is for a specific time period—known as fixed-duration therapy—your doctor may choose to use clonoSEQ at these time points3-12.
Initial diagnosis3,4
Identify cancer cell DNA (Clonality ID test)
This clonoSEQ test provides a baseline. Because this test will have the largest number of cancer cells, it helps clonoSEQ know which cells to look for in later tests. Using this same sample, clonoSEQ also analyzes your IGHV mutation status, another important factor in how well you may respond to certain treatments.*
*IGHV testing is available as a CLIA-validated LDT and has not been cleared or approved by the FDA.
During therapy4
You may receive a combination of different therapies over the course of a year; your doctor may test MRD multiple times throughout the course of treatment to see how you are responding.
MRD testing with clonoSEQFollowing therapy3
Another test when you finish therapy will show how effective it was.
MRD testing with clonoSEQPeriodically3,4
Regular tests to check for MRD can inform you and your doctor whether any cancer has returned.
MRD testing with clonoSEQclonoSEQ in action:
A case study
Let’s look at how clonoSEQ helped a patient like you.
Remember, this is only 1 example—and clonoSEQ has helped people with many different CLL profiles.
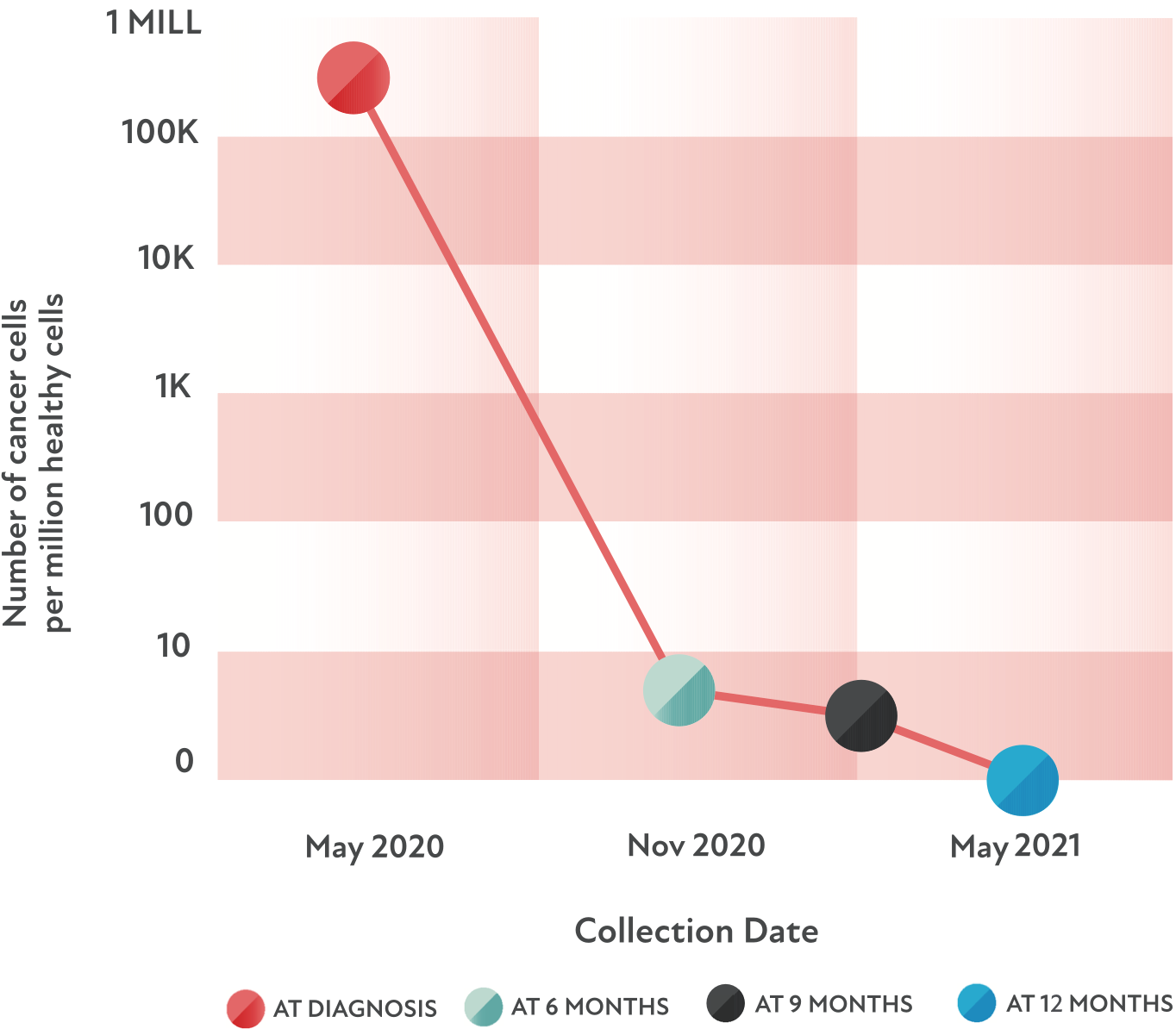
This is for illustration purposes only. The actual clonoSEQ report will look different, as shown here.
- The patient: A 68-year-old man with no significant complications
- The goal: For no detectable MRD to be present
- The treatment: A 1-year course of fixed-duration therapy
- The result: Undetectable MRD (uMRD) after 1 year of treatment
The patient and his doctor decided to continue monitoring with clonoSEQ every 6 months to be aware of any potential changes.
If you have CLL, talk with your doctor about clonoSEQ. Pinpoint where you are—and come up with a plan that works for you.
Questions to ask your doctor
This page is intended for a US-based audience.
clonoSEQ® is an FDA-cleared test used to detect minimal residual disease (MRD) in bone marrow from patients with multiple myeloma or B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) and blood or bone marrow from patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). clonoSEQ is also available for use in other lymphoid cancers and specimen types as a CLIA-validated laboratory developed test (LDT).
clonoSEQ is only available by prescription from a licensed healthcare professional. Results may vary. Talk to your healthcare provider to see if clonoSEQ testing is right for you. For important information about the FDA-cleared uses of clonoSEQ including test limitations, please visit clonoSEQ.com/technical-summary.
References
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia. NCCN Guidelines®. Accessed November 9, 2021. https://www.NCCN.org/patientresources/patient-resources/guidelines-for-patients
- clonoSEQ®. [technical summary]. Seattle, WA: Adaptive Biotechnologies; 2020. https://www.clonoseq.com/technical-summary
- Referenced with permission from the NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®️) for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma V.1.2024. ©️ National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc. 2023. All rights reserved. Accessed Nov. 20, 2023. To view the most recent and complete version of the guideline, go online to NCCN.org. NCCN makes no warranties of any kind whatsoever regarding their content, use or application and disclaims any responsibility for their application or use in any way.
- Al-Sawaf O, et al. Lancet Oncol. 2020;21(9):1188-1200.
- Al-Sawaf O, et al. ASH 2020. Abstract 127. Accessed September 2, 2021.
https://ash.confex.com/ash/2020/webprogram/Paper136977.html
- Al-Sawaf O, et al. ASH 2020. Abstract 1310. Accessed September 2, 2021. https://ash.confex.com/ash/2020/webprogram/Paper134865.html
- ClinicalTrials.gov. NCT04560322. Accessed November 4, 2021. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04560322?term=NCT04560322&draw=2&rank=1
- Hallek M, et al. Blood. 2018;131(25):2745-2760.
- Eichhorst B, et al. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17(7):928-942.
- Goede V, et al. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(12):1101-1110.
- Hillmen P, et al. Lancet. 2015;385(9980):1873-1883.
- Fischer K, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(26):3209-3216.
